The compressor is often seen as a bit of a mysterious effect. I will try here to enlighten those of you who think “why the heck should I be using a compressor?”. You will also find below a video demo showing what a compressor does to your guitar tone.
Studio Compressors vs Guitar Compressors
You have first to understand a little bit about how a compressor works. Compressors originated in studios as sound reinforcement tools. They are probably the most used studio processors after equalizers and reverbs. What they do is “reduce the dynamics range of a signal” i.e. the difference between the softest and loudest volumes. In simpler terms, when you feed a signal to a compressor, be it vocals, drums, guitar or bouzouki and the volume of this signal is louder than a “threshold”, the compressor will make it softer. The amount of reduction is governed by a setting called “ratio”. In that respect a compressor can do what a limiter does, there is a quite loose difference between the two. The original use of compressors was to avoid distorting recordings or radio emissions. But a compressor can also have the effect of augmenting the sustain by increasing the volume as the signal fades out (this is very useful with a guitar, more on that later).

Beside “threshold” and “ratio” settings, there is also usually an “attack” setting (how fast the compressor kicks in) and a “release” setting (which can increase the perceived sustain). I will not really go into more details as this post is guitar oriented and studio compression is a very vast subject. Nevertheless, know that compressors are used in studios on almost every instrument as well as entire mixes to add punch, clarity, smoothness, more perceived volume, etc. If you are serious about making your own recordings, you will have to master the art of compression (see this MIX magazine article for further reference).
It is indeed quite an art to find the correct compression settings on studio compressors so that the sound does not appear too compressed i.e. so that the use of compression is transparent. On extreme settings, it will become more like an effect than a transparent sound reinforcement tool. It will generate a “squashed” sound which happens to sound pretty good with a guitar.
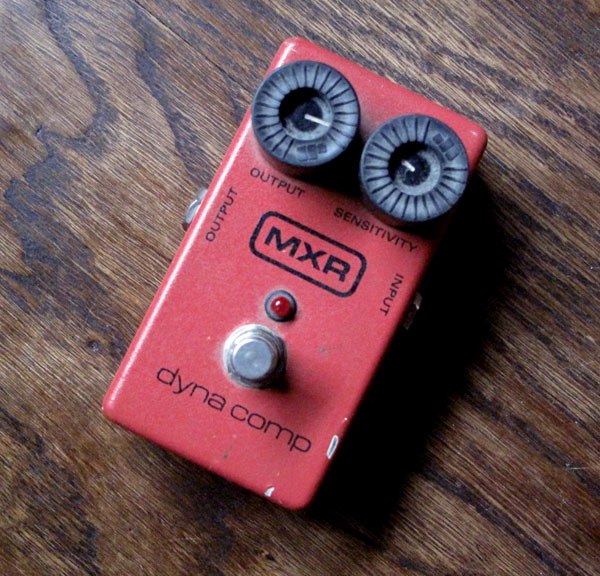
This is why effect manufacturers have put compressors into pedals, fortunately with simplified settings compared to their studio counterparts. They are also adapted to the dynamics and frequency range of a guitar and would not compare to their more versatile studio cousins in terms of sheer audio quality. The most famous of all compressors for guitar, the MXR dynacomp, has only two settings: output volume and “intensity” which controls the amount of compression. The more you turn it clockwise the more your tone will sound “squashed”.

Where do I plug a compressor in the effect chain?
It usually goes at the beginning of the chain before overdrive and distortion effects. You can refer to my previous post about effect placement. If you look at a multi effect unit, you will actually see that the compressor is often first in the chain. I have also written a previous post about the unconventional use of a guitar compressor at the end of the chain in a recording situation.
And what does a compressor do to my guitar tone?
Used with a clean tone, a compressor will give you a bit of a “clicky” tone with lots of sustain. David Gilmour of Pink Floyd has been a long time user of compressors to get more sustain on his clean tone. He has used an MXR Dynacomp for a long time and is now using a quite expensive Demeter Compulator. Country guitarists make heavy use of compressors for their fast clean licks, adding an almost liquid quality to them. Funk and pop guitarists also use them to give some edge and volume consistency to their rhythm guitar runs.
Used before a distortion or overdrive, a compressor will be harder to notice as these effects already feature quite some natural compression. Nevertheless, a compressor can bring more sustain and fatness. Be careful about one thing though, by their very nature, compressors tend to add some hiss.
Demo
Here is an MXR Dynacomp compressor in action with my trusty Stratocaster and Fender Champ amplifier. I have set the OUTPUT and SENSITIVITY at 2 o’clock on the compressor which is quite high, the idea here was to exaggerate a little to demonstrate the effect. In the first part of the video, I show how it sounds with a clean sound. Note the “clicky” tone it produces as well as the increased sustain. In the second part, I show how it sounds used with a Tube Screamer placed after. Not so obvious to spot but it does fatten the tone and give it a little more sustain:
Short list of compression pedals
- The MXR Dynacomp is a very common compressor and was used by almost everybody in the 70s/80s including David Gilmour. It is still widely used by pros today. MXR sells two different versions: the modern one and the 76 reissue. The latter is a limited run and is meant to be closer to the early Dynacomps (and also unfortunately lacks a LED). I personally own a “modern” one from 1995. The Dynacomp is neither the most silent nor the most hi definition piece of gear but it has real character which is why it is so popular. Mine tends to be a bit bassy also which means the tone gets quite fat.
- The BOSS CS-3 is a quite clean compressor but does not have much character in my opinion. I had mine modified with the Opto plus Monte Allum modification and it has turned it in an almost studio grade compressor.
- Electro-Harmonix has several compressors in their line-up including the tube based Black Finger and the compact Soul Preacher.
- The Keeley Compressor is effect guru Robert Keeley’s most popular pedal. This boutique compressor has quite a following now.
- The Analogman mini-Bicomprossor is another powerful boutique pedal featuring two compressors in one (I don’t have one but it is no secret I am a big fan of Analogman’s stuff so it must be pretty awesome).
- The Demeter Compulator is another high end compressor pedal, notably used by David Gilmour after he ditched his Dynacomp.
This is not by any stretch an exhaustive list as virtually every pedal manufacturer has at least one compressor in its range.
Hopefully this post will encourage you to experiment with compressors.
Woweee!! This sounds super cool Romain. Thank you for the hospitality on the shoot yesterday. We are looking forward to checking out more of your stuff on the site here!
Thank you! You indeed have encouraged me! 😀
thanks a bunch, this is very helpful! I’m wondering if you know what sort of effects David Gilmour is using in in the song “coming back to life” on the album “the division bell”. I’m thinking theres a compressor in there along with the delay?
Thank’s, great article. I have a cheap compressor now but plan to make it a priority to get a better one. Thanks
Well done. Just bought a Dbx MC6 for 5 bucks and been wondering what it does.
Here we go…
Do you leave the Compressor ‘on’ all the time or just for ‘soloing’ ?
Personally, I only used from time to time. Some people leave their compressor on all the time.
When I turn on my compressor, I can hear radio in my amp. What’s wrong? BTW I paid 100 bucks for it and now I’m not happy with it…
What kind of guitar do you use? What kind of pickups? Do you not get the radio at all without the compressor? There are many reasons why you’d get the radio through your guitar rig: bad cables, earthing problems with the electricity in your house, single coil pickups, etc.
+1 on the Monte Allums Boss compressor mod. I bought a Boss compressor and used it for about a week and then put it back in it’s box where it sat for a couple years. Upon cleaning up my gear room I found it and decided to give it another try. It was awful. It hissed when using other pedals and the knobs didn’t really do all that much. So I started reading about it and learned of the mod and gave it a try. The difference was overwhelmingly night and day and now it’s a mainstay on my board and gets almost constant use.
I use the MXR Dynacomp. I’ve been using an AC15, and running the dynacomp super high to drive the amplifier to a distorted level.
I’ve upgraded my amplifier though to the AC30, which is actually too loud for the arrangement I’m playing in. The AC30 provides control of an over driven channel through the ‘top boost’ feature. The problem is, playing at a volume that is acceptable compromises the amplifier tone and the level of my leads.
What are your thoughts about using the compressor output feature as almost a ‘limiter’ to pull the over all volume of the amp back, allowing me to keep the amp super hot, and still have plenty of head room for my leads to jump out?
Yes, it’s one way to use it. Paul Gilbert use something called the Detox EQ for the same effect, check it out.
Thank you so much for simplifying the guitar Compressor for me. I to use the MXR DYNA COMP. You really did help a lot. Thanks again.
great article, but what about the Boss CS-2, David gilmour used it post Floyd until mid 90’s ? do you have personal opinion about it ?
It’s suppoed to be a great comp but I have never used it personnally. Checkout gilmourish.com or kitrae.net.
I want to get rid of “clicky” but keep the benefits of compression…do I need a pre-compression compression (two compressors in front of the chain)? Like how Gilmore’s notes on some songs seem to drop from nowhere completely absent of pick attack or “click”…that’s what I’m trying to get. Any ideas?